Difference between revisions of "Spain:Spain"
| Line 117: | Line 117: | ||
|- | |- | ||
!Acronym | !Acronym | ||
|AESAN | |AESAN OA | ||
|- | |- | ||
!Activities | !Activities | ||
| | | | ||
*Risk assessment | *Risk assessment | ||
*Risk management | |||
*Risk communication | *Risk communication | ||
*Codex Contact Point | *Codex Contact Point | ||
*EFSA Focal Point | *EFSA Focal Point | ||
*RASFF | *RASFF Contact Point | ||
|- | |- | ||
!Responsibilities | !Responsibilities | ||
| Line 135: | Line 135: | ||
|- | |- | ||
!URL | !URL | ||
| | |https://www.aesan.gob.es/en/AECOSAN/web/home/aecosan_inicio.htm | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 13:02, 8 November 2022
© worldfoodsafetyalmanac.bfr.berlin
Regulation (EC) No 178/2002, together with Law 17/2011 of 5 July on food safety and nutrition, are the foundations of food safety in Spain.
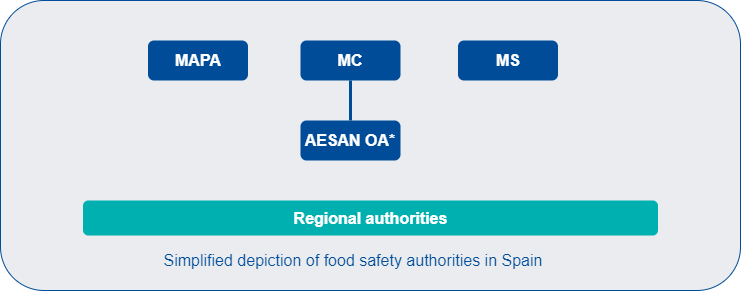
The Spanish Food Safety and Nutrition Agency (AESAN OA), together with the Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries and Food (MAPA) and the Ministry of Health, is responsible for the coordination of the food safety control systems at national level. Regional authorities are responsible for the implementation of official controls of food safety within their territory.
All the information regarding the organization of the food control system in Spain is included in the Spanish Multiannual National Control Plan, called Plan Nacional de Control Oficial de la Cadena Alimentaria (PNCOCA 2021-2025), available in English in this link.
AESAN OA is an autonomous body belonging to the Ministry of Consumer Affairs and functionally reports to the Ministry of Consumer Affairs, the Ministry of Health, and the Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries and Food.
Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries and Food
| Name | Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries and Food |
|---|---|
| Acronym | MAPA |
| Activities |
|
| Responsibilities | |
| Location | Madrid |
| URL | https://www.mapa.gob.es/en/ |
The Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries and Food (MAPA) is responsible for agricultural policy, animal health, food safety in primary production, plant health, animal welfare, food quality and fraud control in the food industry. MAPA prepares draft national legislations and is responsible for the coordination of official controls, including import and export controls within the scope of its competency.
MAPA is the national contact point for food fraud and for the RASFF (feed), and is a user of the Administrative Assistance and Cooperation System (AAC system).
MAPA is also responsible for the preparation of the risk assessments of plant protection products residues and animal feed, and is also in charge of regulating the use of plant protection products.
The scope of MAPA’s competencies also covers national decisions on GMOs, through the Interministerial Council on GMOs, on zoonoses as well as on the distribution, prescription, dispensing and use of veterinary medical products. It is also the regulatory authority for pesticides (registration, authorisation and monitoring of use). However, before MAPA authorises the use of pesticides, AESAN OA is consulted with regard to residues in foods, the Ministry of Health is consulted to assess the safety of the user, and MAPA assesses the efficacy of the pesticide in question and its safety for the environment.
MAPA has four National Reference Laboratories, in compliance with Regulation (EU) 2017/625:
- Central Veterinary-Animal Health Laboratory (Algete)
- Central Veterinary-Molecular Genetic Laboratory
- Central Animal Health Laboratory (Santa Fé)
- EU Reference Laboratory for African Horse Sickness and Bluetongue.
Ministry of Health
| Name | Ministry of Health |
|---|---|
| Acronym | MS |
| Activities |
|
| Responsibilities | |
| Location | Madrid |
| URL | https://www.mscbs.gob.es/en/sanidad/portada/home.htm |
The Ministry of Health (MS) deals with public health policy. Furthermore, the Sub-Directorate General of Foreign Health, a dependent body in this Ministry’s General Directorate of Public Health, is responsible for food safety concerning imports and exports of food, including products of animal and non-animal origin and composite products, food contact materials, and animal by-products for the manufacture of pharmaceuticals, cosmetics and medical devices for medical purposes.
The regulatory authority for medicines and medical products for human and veterinary use is the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products, a dependent body in the Ministry of Health.
Ministry of Consumer Affairs
| Name | Ministry of Consumer Affairs |
|---|---|
| Acronym | MC |
| Activities |
|
| Responsibilities | |
| Location | Madrid |
| URL | https://www.consumo.gob.es/en |
The Ministry of Consumer Affairs (MC) is responsible for consumer protection, the development of consumer affairs policies, and defending the rights of the consumers. It also drafts national legislation and is the contact point for RAPEX and a user of the Administrative Assistance and Cooperation System (AAC system). Within the Ministry of Consumer Affairs, AESAN OA is responsible for all matters relating to food safety.
The Ministry of Consumer Affairs (MC) is responsible for the proposal and execution of the National Government's policy on consumer affairs, consumer rights protection and gambling activities at national level.
The General Secretariat of Consumer Affairs and Gambling of the MC is made up of three bodies: The General Directorate of Consumer Affairs, the General Directorate for the Regulation of Gambling and AESAN, an autonomous body which is organically attached to this general secretariat. The Head of the General Secretariat is also the President of AESAN OA.
The General Directorate of Consumer Affairs (DGC) is responsible for consumer rights protection and the development of consumer affairs policies. It establishes and promotes consumer protection policies in coordination with the autonomous communities (Spanish regions). The DGC is a user of the Administrative Assistance and Cooperation System (AAC system) for non-compliances regarding food mislabeling and food quality and AAC-FF for food fraud cases, both systems integrated in the iRASFF system. It is also the contact point of Rapid Exchange of Information System (RAPEX) for unsafe consumer products and consumer protection.
Spanish Agency for Food Safety & Nutrition
| Name | Spanish Agency for Food Safety & Nutrition |
|---|---|
| Acronym | AESAN OA |
| Activities |
|
| Responsibilities | |
| Location | Madrid |
| URL | https://www.aesan.gob.es/en/AECOSAN/web/home/aecosan_inicio.htm |
AESAN is the competent authority for the coordination of food safety within the Ministry of Health and for risk assessments.
AESAN is supported by a Scientific Committee comprised of independent external experts in the area of food safety and nutrition who are commissioned to draft risk assessment reports. The Scientific Committee issues updated scientific reports on biological, chemical, technological and nutritional hazards.
AESAN also prepares recommendations for the reduction of risks and identifies new health risks.
AESAN is also responsible for the risk management of biological, chemical and nutritional hazards and participates in decision-making on GMOs in foods in the Interministerial Council on GMOs.
AESAN is the competent authority for all draft legislations relating to the safety of foods available in Spain, which includes the transposition of EU directives into domestic legislation and the preparation of draft legislations at the national level.
It is also the competent authority in matters relating to food safety responsible for the coordination of official controls in Spain, and for the coordination and programming of official controls on food safety. It also prepares the National Official Control Plan and its corresponding annual reports in collaboration with MAPA and MS.
AESAN also acts as the national contact point for RASFF and is a user of the Administrative Assistance and Cooperation System (AAC system).
The remit of AESAN also includes the design and management of communication strategies in relation to food risk, establishing precise mechanisms that facilitate transparent communication of consumer safety risks to the general public, the scientific community and other involved or interested groups.
AESAN’s area of work extends beyond food safety to nutrition, physical activity and healthy eating habits.
AESAN has two National Reference Laboratories in compliance with Regulation (EU) 2017/625. These are the National Reference Laboratory (National Centre for Food (CNA)) and one EU Reference Laboratory for Marine Biotoxins (EURLMB).
Regional and local levels
From an administrative point of view, Spain is organised at the regional and local level into 17 autonomous communities, two autonomous cities (Ceuta and Melilla) and 52 provinces. Some regional food safety authorities conduct risk assessments at the local level. The implementation of official controls for food and feed, animal health, animal welfare and plant health is the responsibility of the regional authorities.
Article 36 institutions
| Institutions involved in the EFSA network pursuant to Article 36 Reg. (EC) No. 178/2002 |
|---|
|