Latvia
© worldfoodsafetyalmanac.bfr.berlin
Food businesses have to follow both the EU food safety legislation and the national legal acts in the area of food safety and quality. The Law on the Supervision of the Handling of Food is the central foundation for food legislation in Latvia. Infringement of food safety regulations concerning routine checks of food establishments, consumer complaints and outbreaks of foodborne diseases can lead to measures under civil law and, if necessary, under criminal law. Official controls in the area of food safety are carried out on the basis of the risk assessment approach. However, the final decision on the legality of governmental measures rests with the courts.
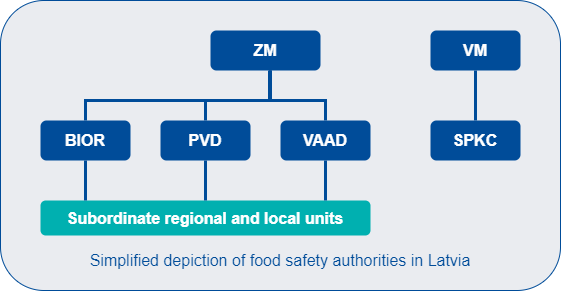
In Latvia, there is clear institutional separation with regard to the implementation of risk assessment and risk management functions in the area of food safety. Risk assessments are conducted by the Institute of Food Safety, Animal Health and Environment (BIOR), while risk management rests with the Food and Veterinary Service of Latvia. Urgent information with regard to risk assessment and risk management activities, as well as other relevant information for food business operators and consumers is published on the Internet homepage of the competent authorities on a case-by-case basis unless there are statutory provisions that prohibit it.
Ministry of Agriculture
| Name | Ministry of Agriculture |
|---|---|
| Acronym | ZM |
| Activities |
|
| Responsibilities | |
| Location | Riga |
| URL | https://www.zm.gov.lv/en/ |
The Ministry of Agriculture (ZM) is responsible for the development and implementation of policy in agricultural and food and feed safety sectors, including drafting national legal acts for the sectors mentioned above. The ZM cooperates with BIOR as the risk assessment body and with the Food and Veterinary Service and State Plant Protection Service as risk management bodies to decide on necessary measures for risk management purposes. The ZM is constantly involved in risk communication activities at different levels.
In general, the portfolio of the ZM covers topics such as food safety and quality, plant health and plant protection, animal health and animal welfare. The ZM’s responsibilities include legal regulation of novel foods, food supplements, genetically modified organisms (GMOs), mineral water, as well as development and implementation of monitoring and control programmes in the area of zoonoses, pesticide residues, residues of veterinary drugs and other food and feed contaminants.
Ministry of Health
| Name | Ministry of Health |
|---|---|
| Acronym | VM |
| Activities |
|
| Responsibilities | |
| Location | Riga |
| URL | http://www.vm.gov.lv/en/ |
The main task of the Ministry of Health (VM) is to develop and implement national policy to safeguard public health and to promote disease prevention by encouraging healthy lifestyles, as well as to create conditions for citizens to receive cost-effective, accessible and quality health care services.
The VM is responsible for the development, coordination and updating of nutrition policy, analysis of the results of foodborne disease monitoring, as well as the preparation of scientific opinions in relation to solving nutrition problems and providing the public with information on current nutrition topics.
The VM is responsible for elaborating recommendations for nutrient and energy intake for different population groups in Latvia and for the development of standards for nutrient and energy intake for children in preschool and school, as well as for residents of social care houses and patients in hospitals.
The VM is involved in the monitoring of the safety and quality of drinking water, with the exception of internal water supplies for food establishments. The Nutrition Council under the VM was set up to support the activities in the field of nutrition.
The VM is constantly involved in risk communication activities at different levels.
Institute of Food Safety, Animal Health and Environment
| Name | Institute of Food Safety, Animal Health and Environment |
|---|---|
| Acronym | BIOR |
| Activities |
|
| Responsibilities | |
| Location | Riga |
| URL | https://bior.lv/en |
The Institute of Food Safety, Animal Health and Environment (BIOR) carries out scientific activities in the food, veterinary, environmental and fishery sectors, as well as in other sectors related to biology. BIOR provides expertise, scientific substantiation and risk assessments in the sectors mentioned above. BIOR implements projects to assess the risk in the field of food safety and animal infectious diseases, ensuring cooperation with institutions and organisations performing activities in these areas. BIOR performs functions of the National Reference Laboratory in the areas defined in the legislation and conducts laboratory and diagnostic investigations related to state monitoring and food movement control, animal health protection, animal feed and veterinary medicine movement. BIOR is Latvia's designated National Focal Point for the EFSA.
Food and Veterinary Service
| Name | Food and Veterinary Service |
|---|---|
| Acronym | PVD |
| Activities |
|
| Responsibilities | |
| Location | Riga |
| URL | https://www.pvd.gov.lv/en |
The Food and Veterinary Service (PVD) operates under the supervision of the Ministry of Agriculture. The PVD is responsible for the realisation of the state's surveillance and control function in the area of food safety and quality, as well as in the area of food labelling throughout the entire food chain, including surveillance and border controls of food (“from the field to the table” concept). The PVD is also in charge of the registration and approval of food establishments.
If there is a threat to human life or health, the state's chief food and veterinary inspector is entitled to specify restrictions or prohibitions on the distribution of food in the territory of Latvia. The PVD is nominated as the official RASFF contact point in Latvia.
State Plant Protection Service
| Name | State Plant Protection Service |
|---|---|
| Acronym | VAAD |
| Activities |
|
| Responsibilities | |
| Location | Riga |
| URL | https://www.vaad.gov.lv/en |
The State Plant Protection Service (VAAD) operates under the supervision of the Ministry of Agriculture. The VAAD is responsible for official surveillance and controls in the area of free movement of plant products, fertilisers, plants and plant protection products, plant varieties, seed and planting material. The VAAD collaborates with international organisations and exchanges information with other countries on issues concerning plant protection, plant quarantine, movement of seeds and variety protection rights. The VAAD is responsible for the control of GMOs within seeds and other propagating material.
Centre for Disease Prevention and Control
| Name | Centre for Disease Prevention and Control |
|---|---|
| Acronym | SPKC |
| Activities |
|
| Responsibilities | |
| Location | Riga |
| URL | http://www.spkc.gov.lv |
The Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (SPKC) conducts epidemiologic surveillance and monitoring and maintains related databases, as well as takes the necessary measures to prevent and localise infectious diseases. It carries out public health monitoring, maintains the related reporting system and advises and informs the public on health and healthy lifestyle issues. The SPKC is responsible for the Early Warning and Response System for communicable diseases in the EU (EWRS), performs the tasks of the coordinator of The European Surveillance System (TESSy) and is designated as a Focal Point for WHO and the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control.
Article 36 institutions
| Institutions involved in the EFSA network pursuant to Article 36 Reg. (EC) No. 178/2002 |
|---|
|