Ministry of Health
- Risk assessment
- Risk communication
- Risk management
- EFSA Focal Point
- RASFF contact point
- Health policy, food safety
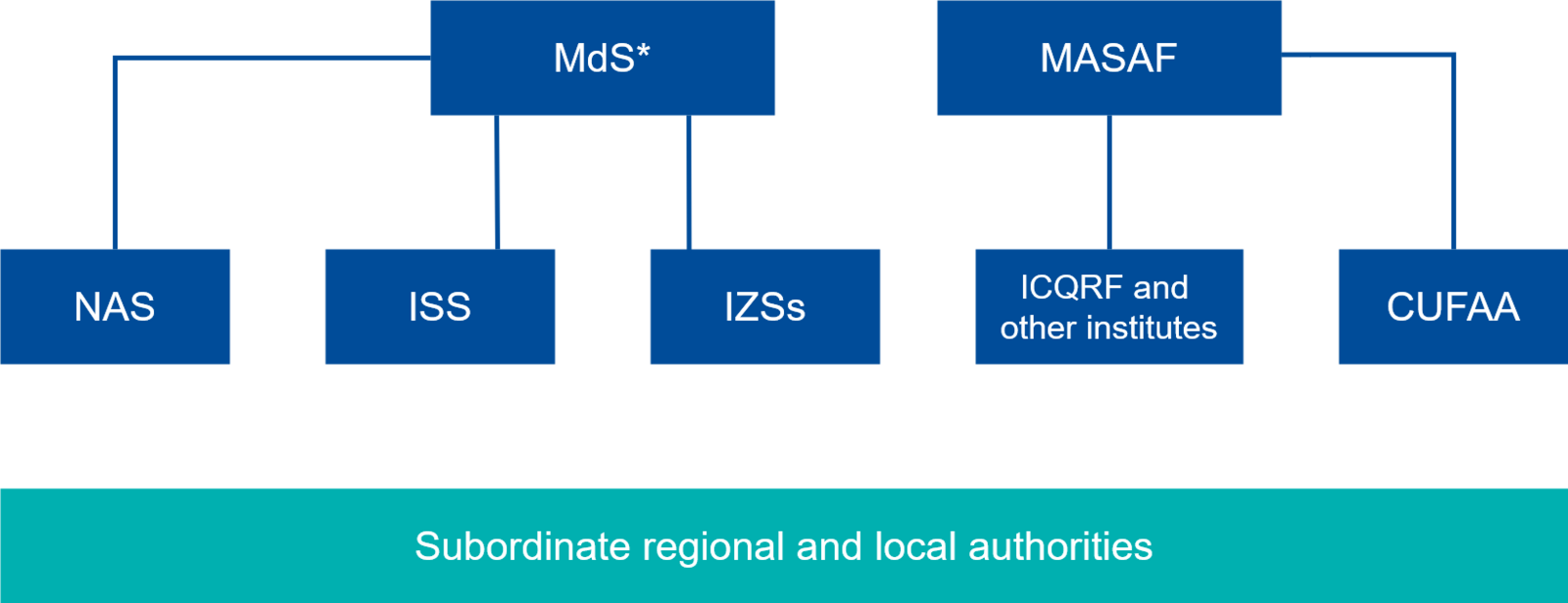
In Italy, most of the mandates for food and feed safety, animal health and animal welfare are assigned at the national level to the Ministry of Health (MdS), recently reorganised by the Decree of the President of the Council of Ministers No. 196 of 30 October 2023. In particular, the aforementioned responsibilities fall under the remit of the Department for Human Heath, Animal Health and the Ecosystem (One Health) and International Relations (DOHRI), with its Directorates-General:
- Directorate-General for Animal Health (DGSA)
- Directorate-General for Food Hygiene and Safety (DGISAN)
- Directorate-General for Healthy Lifestyles and Relations with the Ecosystem (DGCSV)
As regards risk assessment, the Department for Human Heath, Animal Health and the Ecosystem (One Health) and International Relations (DOHRI) is the national reference authority for the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), with the support of the Directorate-General for Healthy Lifestyles and Relations with the Ecosystem (DGCSV). In particular, the DGCSV performs the functions of EFSA Focal Point and support to the EFSA Advisory Forum through its Office 3.
In addition, the DGCSV is responsible for coordinating risk assessment processes and implementing risk assessments for physical, chemical and biological hazards for food safety purposes, as well as for consulting with consumer and producer associations. All activities related to risk assessments and consultations with associations are carried out with the support of the two specific sections of the National Committee for Food Safety (CNSA). In particular, the Food Safety Section provides scientific advice at the request of the central Competent Authorities as well as the Competent Authorities of the regions and autonomous provinces.
The DGSA and the DGISAN perform the funcions assigned to the DOHRI with regard to risk management in the fields of food and feed safety, animal health and animal welfare, both domestically and at the import stage.
In view of the division of competencies provided for by national legislation, official controls on the territory are planned and carried out by the regional and local Competent Authorities on the basis of guidelines issued by the Ministry.
The remit of the MdS includes official controls during import of food and feed, general food and feed hygiene, novel food, food supplements, labelling and nutrition, food contact materials, genetically modified organisms (GMOs), zoonoses, residues of plant protection products, and veterinary medicinal products. In addition, the MdS is the regulatory authorithy for plant protection products and veterinary medicinal products, and may conduct inspections and audits of the regional Competent Authorities.
Italy introduced administrative sanctions against violations of Regulation (EC) No. 178/2002 by Legislative Decree No. 190/2006, and implemented the EU Hygiene Package by Legislative Decree No. 193/2007 (amended by Legislative Decree No. 27/2021), which identifies the national Competent Authorities for official controls. In cases where an identified nonconformity may pose a risk to public health, criminal charges may also be brought.
All control activities in the field of food safety are integrated in a Multi-Annual National Control Plan (MANCP) developed in compliance with Title V of Regulation (EC) No. 2017/625.